IP QoS Tester
Quality of Service (QoS) measurement for IP transmissions
IP QoS Tester is a very easy solution to measure the most important parameters concerning Quality of Service (QoS) over IP networks.
IP QoS Tester enables you to monitor the quality of the connection between different machines or different sites of your company or organization.
IP QoS Tester exists for Raspberry Pi, Linux and Windows.
IP QoS Tester is a console application (with a web interface) on Raspberry Pi and Linux, and an application with a GUI on Windows.
On Raspbery Pi, IP QoS Tester is extremely convenient, with the following features:
- You can measure UDP packets loss, delay, jitter (mean and max), corruption, re-ordering (mean and max)
- You can define the value of the DSCP field (the field in IP packets for QoS)
- Works with Ethernet and/or Wifi
- Small
- Cheap
- Low-consuption
- Light-weight
- Fan-free
- 24/7/365 IP QoS monitoring
- Web interface
- API
IP QoS Tester enables testing and monitoring of IP connections, effectively replacing tools such as ping, iperf, nping, and ncat.
The screenshots presented on this page come from the Windows version. The Linux and Raspberry Pi versions don't use a GUI (they are command line tools).
Overview
IP Qos Tester is a solution containing three applications:
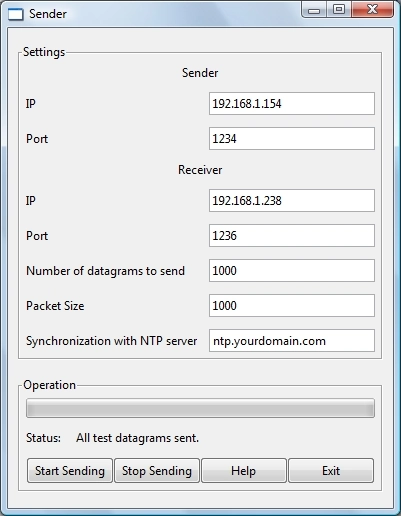
- the Sender application
- the Receiver application
- the Reflector application
The Sender application sends UDP datagrams to the Receiver application (identified by its IP address and its user-defined port number). Between the Sender and Receiver applications, the Reflector application can serve as an intermediary by reflecting the data it receives (from Sender) towards another machine (running Receiver).
The user can choose the value of the DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) field of sent UDP packets. The DSCP is a field in the IP header that enables the classification and marking of network traffic for quality of service (QoS) purposes, allowing routers and switches to prioritize and manage packet delivery based on specific service requirements.
The user can choose the size of the datagrams and the number of the datagrams to send during a test.
Measured parameters
If the size of a datagram is lower or equal to the MTU, then Sender and Receiver work on a packet basis (instead of a datagram basis).
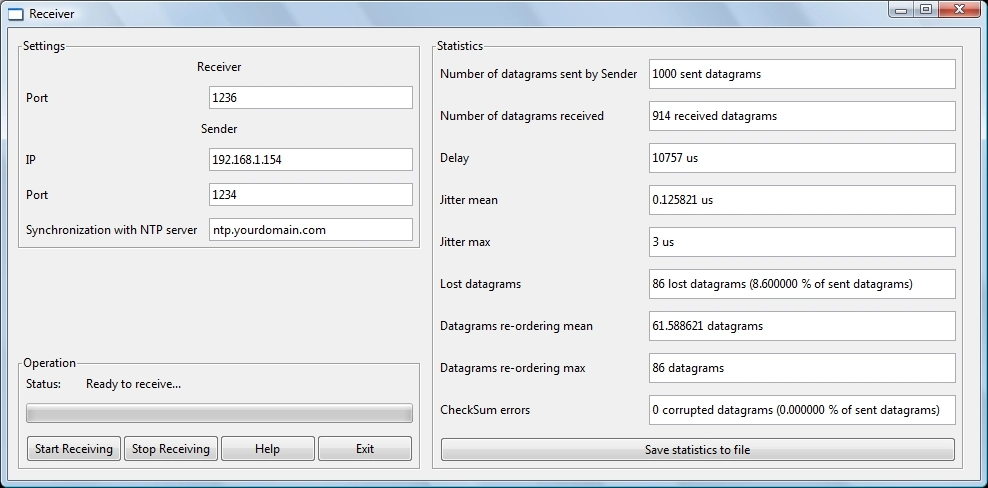
The Receiver checks the received packets and measures the most important parameters concerning QoS:
- Packet (or datagram) loss : number of lost packets (or datagrams) and percentage of lost packets (or datagrams)
- Packet (or datagram) corruption : number of corrupted packets (or datagrams) and percentage of corrupted packets (or datagrams)
- Packet (or datagram) delay, in microseconds
- Packet (or datagram) jitter, in microseconds
- Packet (or datagram) reordering
The Receiver can send you email alerts if some measured values go beyond a threshold (defined by the user) during a certain duration (also defined by the user).
The Receiver also runs its own web server (on the port of your choice) so that you can check the measures in real time and inject them in your own monitoring system.
Conclusion
IP QoS Tester is a set of 3 tools: Sender, Receiver and Reflector.
IP QoS Tester measures the packets loss, delay, jitter (mean and max), reordering (mean and max) and corruption of packets sent from one machine to another.
There are two ways to use IP QoS Tester:
- You install the Receiver tool on one machine (a server for example) and the Sender tool on the other (a client). But to do that, you have to make sure that the two machines have their clocks synchronized with an NTP server (IP QoS Tester enables you to do that, you just have to provide the URL of a NTP time server - and there are many public NTP servers).
- You install the Sender tool and the Receiver tool on the same machine (a client for example) and the Reflector tool on the other (a server). When it receives packets (from the Sender tool), the Reflector tool will re-send them to the Receiver tool. Of course, the packets received by the Receiver tool will have been transmitted twice (Sender to Reflector, then Reflector to Receiver). Then you have to consider that the real delay between the client and the server is the half of the measured delay (same things for the number of lost packets, reordering, etc.).